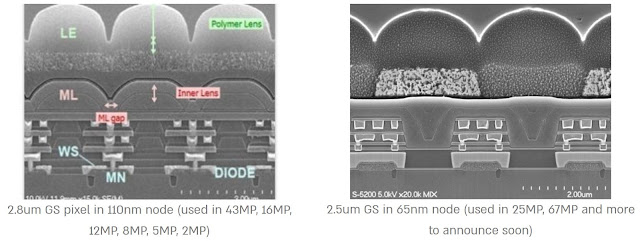
TowerJazz blog post describes the advantages of its 65nm platform, including small global shutter pixels:
"World’s previous smallest GS pixel, also achieved by TowerJazz, was 2.8 µm in 2016 and was based on its 110mm platform. Using the 65nm technology node and optimization of our light pipe technology enabled us a further reduction of pixel size to 2.5um achieving these excellent performance characteristics."
Thursday, February 28, 2019
Yole CCM Industry Report
Yole Developpement publishes a report "Status of the Camera Module Industry 2019 – Focus on Wafer Level Optics." Few quotes:
"The camera module industry has reached a new stage in its development. With $27.1B of global revenues generated in 2018, Yole Développement expects it to maintain a 9.1% Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) for the next 5 years. This industry, which covers image sensors, lenses, voice coil motors, illuminators and camera assemblies, will therefore reach $45.7B by 2024. The overall growth is a combination of mega trends. The main upward driver is the increasing number of cameras in products such as smartphones and cars. 3D sensing cameras are part of this trend, invading mobile devices, computing and automotive industries. If the nature of camera module making is unchanged with 3D sensing, illuminator submodules create a new market area. This brings new technologies, such as wafer level optics (WLO), along with it. The market for devices involved in illumination for 3D sensing accounted for $720M in 2018 and will expand ninefold within five years, reaching $6.1B by 2024. This is helping compensate for the shipment volume slowdown in smartphones, computers, tablet and digital cameras. While the complexity and cost of each individual camera is still increasing on average, reaching $5.5 per unit, we are now seeing more diversity. In recent years the distribution of resolution, optical format and camera type was only heading towards uniformly high specifications. But in 2018 the smartphone market has evolved quite dramatically. In an attempt to work around the increasing cost of imaging, mid-range phones have been implementing 2-5Mp formats that were previously fading away.
This new equilibrium between volume, cost and specification is lowering Yole Développement’s forecast with respect to the previous 2017 report, but overall the direction of the industry remains highly attractive."
"The camera module industry has reached a new stage in its development. With $27.1B of global revenues generated in 2018, Yole Développement expects it to maintain a 9.1% Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) for the next 5 years. This industry, which covers image sensors, lenses, voice coil motors, illuminators and camera assemblies, will therefore reach $45.7B by 2024. The overall growth is a combination of mega trends. The main upward driver is the increasing number of cameras in products such as smartphones and cars. 3D sensing cameras are part of this trend, invading mobile devices, computing and automotive industries. If the nature of camera module making is unchanged with 3D sensing, illuminator submodules create a new market area. This brings new technologies, such as wafer level optics (WLO), along with it. The market for devices involved in illumination for 3D sensing accounted for $720M in 2018 and will expand ninefold within five years, reaching $6.1B by 2024. This is helping compensate for the shipment volume slowdown in smartphones, computers, tablet and digital cameras. While the complexity and cost of each individual camera is still increasing on average, reaching $5.5 per unit, we are now seeing more diversity. In recent years the distribution of resolution, optical format and camera type was only heading towards uniformly high specifications. But in 2018 the smartphone market has evolved quite dramatically. In an attempt to work around the increasing cost of imaging, mid-range phones have been implementing 2-5Mp formats that were previously fading away.
This new equilibrium between volume, cost and specification is lowering Yole Développement’s forecast with respect to the previous 2017 report, but overall the direction of the industry remains highly attractive."
Wednesday, February 27, 2019
Facial Recognition Explained
Youtube Function channel publishes a nice video explaining how facial recognition fuses traditional algorithmic with neural networking:
Other interesting videos on this channel talk about eye tracking observations of soccer player, artists and kids, people at the first date, etc.
Other interesting videos on this channel talk about eye tracking observations of soccer player, artists and kids, people at the first date, etc.
IISW 2019 Pre-Registration Begins
2019 International Image Sensor Workshop (IISW) pre-registration starts now! The Workshop is to be held in Snowbird, Utah on June 23-27.
Registration is limited to approximately 160 attendees on a first-come, first-served basis. Registration will be guaranteed for presenters, but they are still required to register. Past experience shows that registration is often filled to capacity within a few days’ time. Registration forms are available on the web.
Registration is limited to approximately 160 attendees on a first-come, first-served basis. Registration will be guaranteed for presenters, but they are still required to register. Past experience shows that registration is often filled to capacity within a few days’ time. Registration forms are available on the web.
Tuesday, February 26, 2019
OIS with Invensese-TDK and Cambridge Mechatronics Devices
BusinessWire: TDK-owned InvenSense announces the launch of the industry’s first Cambridge Mechatronics SMA (Shape Memory Alloy) OIS software controller specifically designed to leverage the Qualcomm Sensor Execution Environment for Android flagship smartphones. The solution leverages TDK SMA actuators and TDK’s latest 6-axis CORONA premium motion sensors to provide a software controller based on CML’s innovative SMA image stabilization designs and control logic.
“Unlike other OIS solutions that require a dedicated OIS controller chip, the advantage of TDK’s SMA software controller is that it avoids the need for such a dedicated OIS controller chip,” said Lars Johnsson, senior director of Product Marketing, InvenSense, a TDK Group Company. “This reduces the cost and complexity of developing and commercializing SMA OIS solutions and enables OEMs to accelerate their next-generation imaging flagship launches on select Snapdragon mobile platforms that support the Qualcomm Sensor Execution Environment.”
“Unlike other OIS solutions that require a dedicated OIS controller chip, the advantage of TDK’s SMA software controller is that it avoids the need for such a dedicated OIS controller chip,” said Lars Johnsson, senior director of Product Marketing, InvenSense, a TDK Group Company. “This reduces the cost and complexity of developing and commercializing SMA OIS solutions and enables OEMs to accelerate their next-generation imaging flagship launches on select Snapdragon mobile platforms that support the Qualcomm Sensor Execution Environment.”
Xiaomi and Light Announce Joint Development
Globenewswire: Light Co. and Xiaomi sign an agreement to jointly develop and market new imaging solutions for smartphones. The partnership will see Light bring together its computational imaging technology with Xiaomi’s high-end smartphone devices, enabling the companies to bring to market multi-camera smart devices with DSLR-level capabilities.
“Xiaomi is one of the most innovative smartphone device manufacturers with an incredible pedigree, and we’re excited to enter this partnership with them,” said Dave Grannan, CEO and co-founder, Light. “Light’s computational imaging is forever changing the way our devices see the world, and we look forward to applying our pioneering multi-camera technology and empowering their devices with the imaging solutions of the future.”
“We are thrilled to partner with Light to leverage their advanced imaging solutions for our future devices,” said Zhu Dan, VP, smartphone division, GM of camera department, Xiaomi. “Xiaomi works tirelessly to remain at the forefront of smartphone innovation, and perfecting smartphone photography is a key focus for us. We are excited to work on devices using Light’s technology so our users can produce even more amazing photos.”
“Xiaomi is one of the most innovative smartphone device manufacturers with an incredible pedigree, and we’re excited to enter this partnership with them,” said Dave Grannan, CEO and co-founder, Light. “Light’s computational imaging is forever changing the way our devices see the world, and we look forward to applying our pioneering multi-camera technology and empowering their devices with the imaging solutions of the future.”
“We are thrilled to partner with Light to leverage their advanced imaging solutions for our future devices,” said Zhu Dan, VP, smartphone division, GM of camera department, Xiaomi. “Xiaomi works tirelessly to remain at the forefront of smartphone innovation, and perfecting smartphone photography is a key focus for us. We are excited to work on devices using Light’s technology so our users can produce even more amazing photos.”
Monday, February 25, 2019
PMD Presentation at MWC
PMD publishes a MWC page with the company and its products info:
PMD-Infineon announce the 4th generation of their ToF pixel:
"Infineon presents the fourth generation of its REAL3 image sensor IRS2771C. The 3D Time-of-Flight (ToF) single chip is especially designed to meet the requirements of the mobile consumer device market and, in particular, demand for higher resolutions with small lenses. The wide range of use cases includes secure user authentication like face or hand recognition to unlock the device and confirm payments. In addition, the 3D ToF chip enhances augmented reality, morphing and photo (e.g. bokeh) effects and can be used to scan a room.
Measuring only 4.6 x 5 mm, the image sensor features a 150 k (448 x 336) pixel output that comes close to the HVGA standard resolution. This makes the resolution four times higher than that of most ToF solutions on the market today. The pixel array is highly sensitive to 940 nm infrared light and provides unbeaten outdoor performance. This is enabled by the patented Suppression of Background Illumination (SBI) circuitry in every pixel. Due to its high level of integration, each IRS2771C image sensor is essentially a miniature single-chip ToF camera. This dramatically reduces the overall bill of materials and the actual size of the camera module without compromising on performance and keeping power consumption to a minimum.
Developed in Graz, Dresden and Siegen, Infineon’s new 3D image sensor chip bundles Infineon’s expertise at its German and Austria sites. Samples of the chip will be available in March and volume production is scheduled to start in Q4 2019."
PMD-Infineon announce the 4th generation of their ToF pixel:
"Infineon presents the fourth generation of its REAL3 image sensor IRS2771C. The 3D Time-of-Flight (ToF) single chip is especially designed to meet the requirements of the mobile consumer device market and, in particular, demand for higher resolutions with small lenses. The wide range of use cases includes secure user authentication like face or hand recognition to unlock the device and confirm payments. In addition, the 3D ToF chip enhances augmented reality, morphing and photo (e.g. bokeh) effects and can be used to scan a room.
Measuring only 4.6 x 5 mm, the image sensor features a 150 k (448 x 336) pixel output that comes close to the HVGA standard resolution. This makes the resolution four times higher than that of most ToF solutions on the market today. The pixel array is highly sensitive to 940 nm infrared light and provides unbeaten outdoor performance. This is enabled by the patented Suppression of Background Illumination (SBI) circuitry in every pixel. Due to its high level of integration, each IRS2771C image sensor is essentially a miniature single-chip ToF camera. This dramatically reduces the overall bill of materials and the actual size of the camera module without compromising on performance and keeping power consumption to a minimum.
Developed in Graz, Dresden and Siegen, Infineon’s new 3D image sensor chip bundles Infineon’s expertise at its German and Austria sites. Samples of the chip will be available in March and volume production is scheduled to start in Q4 2019."
Smartphone ToF Camera Use Cases
PRNewswire: LG G8 ThinQ equipped with PMD-Infineon ToF module becomes the world's first smartphone with palm vein authentication. LG's Hand ID identifies owners by recognizing the shape, thickness and other individual characteristics of the veins in the palms of their hands. Simply placing a pre-registered hand in front of the front-facing camera for a split second is all it takes to unlock the LG G8 ThinQ and all its content. Since ToF technology in LG's Z Camera sees objects in 3D and is not affected by ambient light, accuracy is unaffected by light from external sources.
The Z Camera is also implemented to advance the user experience with Air Motion gesture recognition. Without ever touching the phone – useful in scenarios like cooking or cleaning – users can answer or end calls, take screenshots, switch between applications or adjust the volume. Controlling the LG G8 ThinQ is achieved by waving a hand or swiping the air, adding convenience to consumers who are increasingly doing more at home and on-the-go.
The Z Camera is also implemented to advance the user experience with Air Motion gesture recognition. Without ever touching the phone – useful in scenarios like cooking or cleaning – users can answer or end calls, take screenshots, switch between applications or adjust the volume. Controlling the LG G8 ThinQ is achieved by waving a hand or swiping the air, adding convenience to consumers who are increasingly doing more at home and on-the-go.
Sunday, February 24, 2019
Nokia Pureview 9 Features 5 Cameras Powered by Light Co.
TheVerge: HMD Global announces Nokia Pureview 9 smartphone with 5 rear cameras powered by Light Co's Lux Capacitor camera-control chip. All 5 sensors have 12MP resolution, 2 of them are color, while 3 - monochrome. All five cameras shoot with different exposures at the same time. The processing time is quite slow: it takes about 10s to process a single picture and another few seconds to save it in full resolution.
GSMArena reports there is also a 6th camera - the ToF one. Most of other sourced do not confirm that. GSMArena says about the phone production plans:
"But there is also the fact that the Nokia 9 will have a limited production run. Once the stock is depleted - that's it. Nokia may not be producing any more devices. The company hasn't revealed exactly how many units it will produce, though."
GSMArena reports there is also a 6th camera - the ToF one. Most of other sourced do not confirm that. GSMArena says about the phone production plans:
"But there is also the fact that the Nokia 9 will have a limited production run. Once the stock is depleted - that's it. Nokia may not be producing any more devices. The company hasn't revealed exactly how many units it will produce, though."
Huawei Folding Phone Has No Dedicated Selfie Camera
Huawei unveils its foldable smartphone - Mate X that eliminates the need in selfie camera:
Update: Verge: Oppo foldable phone concept design is very similar to Huawei's:
Update: Verge: Oppo foldable phone concept design is very similar to Huawei's:
Byton SUV Features PMD Gesture Recognition Camera
BusinessWire: PMD Technologies and BYTON, China-based electric vehicle maker, announce that PMD's 3D ToF sensors will be used for the in-car gesture control camera system operating the 48-inch Shared Experience Display (SED) in BYTON’s first production model, the M-Byte SUV:
“As cars get more and more functions, natural interactions are becoming an important tool to simplify the human-machine interface. Byton is one of the most innovative players in the field, so the partnership is exciting for pmd as we can showcase the potential of our unique 3D approach including full sunlight, which is difficult for other 3D technologies,” said Bernd Buxbaum, CEO of PMD. “Byton is changing the way consumers interact with an automobile and I am proud that our technology is a part of the M-Byte.”
“As cars get more and more functions, natural interactions are becoming an important tool to simplify the human-machine interface. Byton is one of the most innovative players in the field, so the partnership is exciting for pmd as we can showcase the potential of our unique 3D approach including full sunlight, which is difficult for other 3D technologies,” said Bernd Buxbaum, CEO of PMD. “Byton is changing the way consumers interact with an automobile and I am proud that our technology is a part of the M-Byte.”
Saturday, February 23, 2019
Actlight DPD Article
Laser Focus World publishes Lausanne, Switzerland-based Actlight article "Dynamic photodiodes reach single-photon sensitivity at low voltages, with minimal noise" by Maxim Gureev (Actlight CTO) and Denis Sallin (Director of Engineering). Few quotes:
"ActLight’s dynamic photodiode (DPD) uses a new operating mode that converts light intensity into time.1-3 The applied voltage is not constant, but is switched from reverse to forward bias. Applied forward bias induces a large forward current that doesn’t start immediately, but after a time delay (see Fig. 1). The forward current magnitude is controlled only by the applied voltage, and its value does not depend on the light intensity. In contrast, the delay time (triggering time) is a function of the absorbed light power."
"With CMOS compatibility, a high-amplitude output signal, low noise, and low voltage operation, the DPD can also be tuned to reach single-photon sensitivity. This could dramatically enhance the performance of wearable devices and smartphones."
"ActLight developed an iToF method using its DPD that can be manufactured with a standard CMOS or CMOS Image Sensor (CIS) process. The low-voltage iToF range meter demonstrator allows measurement at distances up to 5 m in a wide range of lighting conditions (see Fig. 3). Furthermore, it has demonstrated full sun (>100 klux) background light immunity."
"ActLight’s dynamic photodiode (DPD) uses a new operating mode that converts light intensity into time.1-3 The applied voltage is not constant, but is switched from reverse to forward bias. Applied forward bias induces a large forward current that doesn’t start immediately, but after a time delay (see Fig. 1). The forward current magnitude is controlled only by the applied voltage, and its value does not depend on the light intensity. In contrast, the delay time (triggering time) is a function of the absorbed light power."
"With CMOS compatibility, a high-amplitude output signal, low noise, and low voltage operation, the DPD can also be tuned to reach single-photon sensitivity. This could dramatically enhance the performance of wearable devices and smartphones."
"ActLight developed an iToF method using its DPD that can be manufactured with a standard CMOS or CMOS Image Sensor (CIS) process. The low-voltage iToF range meter demonstrator allows measurement at distances up to 5 m in a wide range of lighting conditions (see Fig. 3). Furthermore, it has demonstrated full sun (>100 klux) background light immunity."
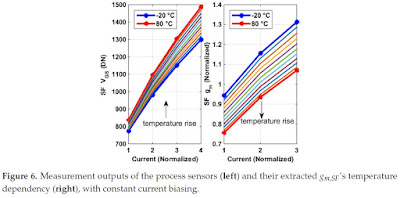
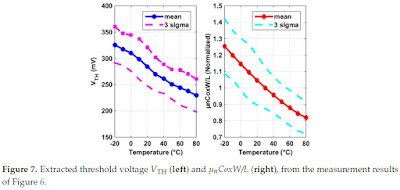
Array Temperature Effects in Pixel and Sensor Performance
MDPI Special Issue "Advanced CMOS Image Sensors and Emerging Applications" publishes a paper "Compensation for Process and Temperature Dependency in a CMOS Image Sensor" by Shuang Xie and Albert Theuwissen from Delft University of Technology and Harvest Imaging.
"This paper analyzes and compensates for process and temperature dependency among a (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) CMOS image sensor (CIS) array. Both the analysis and compensation are supported with experimental results on the CIS’s dark current, dark signal non-uniformity (DSNU), and conversion gain (CG). To model and to compensate for process variations, process sensors based on pixel source follower (SF)’s transconductance gm,SF have been proposed to model and to be compared against the measurement results of SF gain ASF. In addition, ASF’s thermal dependency has been analyzed in detail. To provide thermal information required for temperature compensation, six scattered bipolar junction transistor (BJT)-based temperature sensors replace six image pixels inside the array. They are measured to have an untrimmed inaccuracy within ±0.5 ⁰C. Dark signal and CG’s thermal dependencies are compensated using the on-chip temperature sensors by at least 79% and 87%, respectively."
"This paper analyzes and compensates for process and temperature dependency among a (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) CMOS image sensor (CIS) array. Both the analysis and compensation are supported with experimental results on the CIS’s dark current, dark signal non-uniformity (DSNU), and conversion gain (CG). To model and to compensate for process variations, process sensors based on pixel source follower (SF)’s transconductance gm,SF have been proposed to model and to be compared against the measurement results of SF gain ASF. In addition, ASF’s thermal dependency has been analyzed in detail. To provide thermal information required for temperature compensation, six scattered bipolar junction transistor (BJT)-based temperature sensors replace six image pixels inside the array. They are measured to have an untrimmed inaccuracy within ±0.5 ⁰C. Dark signal and CG’s thermal dependencies are compensated using the on-chip temperature sensors by at least 79% and 87%, respectively."
Friday, February 22, 2019
Non-Destructive Photon Sensing
Intechopen 2018 book "Photon Counting - Fundamentals and Applications" has a chapter "Quantum Non-Demolition Measurement of Photons" (QND) by Keyu Xia from Nanjing University, Nanjing, China. The chapter reviews the possible ways to detect photons without absorbing them that can open a number of interesting opportunities in photon sensing:
"QND measurement opens a door for precise measurement and versatile applications in photon-based quantum information processing. In principle, QND measurement enables repeated measurement of photon number, n, of a light beam. Because QND measurement does not disturb the photon number of light, it allows one to measure the photon number many times. This can surpass the standard quantum limit bounded by the “shot-noise” and allows to measure light with ultrahigh sensitivity. QND measurement down to the single photon level further enables potential application in quantum information processing. Remarkably, when a single signal photon can induce a π phase shift to another probe photon, the scheme for QND measurement essentially has the potential to implement a quantum controlled-phase gate between these two photonic modes. This kind of gate is a universal quantum gate for quantum computation. Another important application is to squeeze light via QND measurement. Although QND measurement has been well studied theoretically and has been realized in experiments, it is still questioned in its interpretation [31]. Monroe comments that photons can be independently generated once a signal photon is detected via absorption. He claims that the concept of QND measurement is confusing and should be demolished. However, his comments are also questionable. Squeezing light through QND measurement cannot be realized by simply generating photons according to the detection events. In summary, the concept of QND measurement applied to photons promises of great applications in quantum measurement. The progress approaching the single photon level may provide a simple router for implementing quantum information processing [32] or even quantum telescope [33]."
"QND measurement opens a door for precise measurement and versatile applications in photon-based quantum information processing. In principle, QND measurement enables repeated measurement of photon number, n, of a light beam. Because QND measurement does not disturb the photon number of light, it allows one to measure the photon number many times. This can surpass the standard quantum limit bounded by the “shot-noise” and allows to measure light with ultrahigh sensitivity. QND measurement down to the single photon level further enables potential application in quantum information processing. Remarkably, when a single signal photon can induce a π phase shift to another probe photon, the scheme for QND measurement essentially has the potential to implement a quantum controlled-phase gate between these two photonic modes. This kind of gate is a universal quantum gate for quantum computation. Another important application is to squeeze light via QND measurement. Although QND measurement has been well studied theoretically and has been realized in experiments, it is still questioned in its interpretation [31]. Monroe comments that photons can be independently generated once a signal photon is detected via absorption. He claims that the concept of QND measurement is confusing and should be demolished. However, his comments are also questionable. Squeezing light through QND measurement cannot be realized by simply generating photons according to the detection events. In summary, the concept of QND measurement applied to photons promises of great applications in quantum measurement. The progress approaching the single photon level may provide a simple router for implementing quantum information processing [32] or even quantum telescope [33]."
Royole Flexible Smartphone Omits Dedicated Selfie Camera
PRNewswire: Royole FlexPai foldable smartphone camera set-up is made up of a 20MP telephoto module, and a 16MP wide-angle module, that can be used for both normal photo shooting or taking a selfie, thanks to the dual view camera mode. There is no dedicated selfie camera in the phone:
Sony Hiring More Image Sensor Engineers in Japan, Expanding Polarization Sensors Lineup
Reuters: Sony Corp swill assign 40% of its new engineer hires in Japan over the next two years to the chip business which includes image sensors, as it looks for growth from new applications in everything from cars to phones. Sony plans to hire 320 new engineers annually in Japan this year and the next, up from 250 in 2018. The figures do not include those to be hired by overseas units.
The allocation is in line with the company’s plans to invest 600b yen ($5.4b) in image sensor business over the three years through March 2021, or half of the group’s planned capital expenditures.
The company cut its annual profit outlook for imaging sensors this month to 130b yen, accounting for just 15% of the Sony Corp.’s overall profit, due to weakening global demand for smartphones.
In another news, Sony adds a second polarization sensor to its portfolio - a 12MP, 1.1-inch IMX253MZR/MYR:
The allocation is in line with the company’s plans to invest 600b yen ($5.4b) in image sensor business over the three years through March 2021, or half of the group’s planned capital expenditures.
The company cut its annual profit outlook for imaging sensors this month to 130b yen, accounting for just 15% of the Sony Corp.’s overall profit, due to weakening global demand for smartphones.
In another news, Sony adds a second polarization sensor to its portfolio - a 12MP, 1.1-inch IMX253MZR/MYR:
Thursday, February 21, 2019
Albert Theuwissen Reviews ISSCC 2019 - Part 3
Albert Theuwissen continues his ISSCC presentations review. The third part covers University of Toronto in cooperation with Synopsys and FBK presentation “Dual-tap pipelined-code-memory coded-exposure pixel CMOS image sensor for multi-exposure single-frame computational imaging” by Navid Sarhangnejad, Nikola Katic, Zhengfan Xia, Mian Wei, Nikita Gusev, Gairik Dutta, Rahul Gulve, Harel Haim, Manuel Moreno Garcia, David Stoppa, Kiriakos N. Kutulakos, and Roman Genov:
Panasonic presentation "A 400x400-Pixel 6μm-Pitch Vertical Avalanche Photodiodes (VAPD) CMOS Image Sensor Based on 150ps-fast Capacitive Relaxation Quenching (RQ) in Geiger Mode for Synthesis of Arbitrary Gain Images" by Yutaka Hirose, Shinzo Koyama, Toru Okino, Akito Inoue, Shigeru Saito, Yugo Nose, Motonori Ishii, Seiji Yamahira, Shigetaka Kasuga, Mitsuyoshi Mori, Tatsuya Kabe, Kentaro Nakanishi, Manabu Usuda, Akihiro Odagawa, and Tsuyoshi Tanaka:
University of Edinburgh, ST, and Heriot-Watt University present “A 246×256 40nm/90nm CMOS 3D-stacked 120dB dynamic range reconfigurable time resolved SPAD imager” by Robert K. Henderson, Nick Johnston, Sam W. Hutchings, Istvan Gyongy, Tarek Al Abbas, Neale Dutton, Max Tyler, Susan Chan, and Jonathan Leach:
Panasonic presentation "A 400x400-Pixel 6μm-Pitch Vertical Avalanche Photodiodes (VAPD) CMOS Image Sensor Based on 150ps-fast Capacitive Relaxation Quenching (RQ) in Geiger Mode for Synthesis of Arbitrary Gain Images" by Yutaka Hirose, Shinzo Koyama, Toru Okino, Akito Inoue, Shigeru Saito, Yugo Nose, Motonori Ishii, Seiji Yamahira, Shigetaka Kasuga, Mitsuyoshi Mori, Tatsuya Kabe, Kentaro Nakanishi, Manabu Usuda, Akihiro Odagawa, and Tsuyoshi Tanaka:
University of Edinburgh, ST, and Heriot-Watt University present “A 246×256 40nm/90nm CMOS 3D-stacked 120dB dynamic range reconfigurable time resolved SPAD imager” by Robert K. Henderson, Nick Johnston, Sam W. Hutchings, Istvan Gyongy, Tarek Al Abbas, Neale Dutton, Max Tyler, Susan Chan, and Jonathan Leach:
Omnivision Announces 1/4-inch 8MP Sensor for Smartphones
PRNewswire: OmniVision announces the OV08B 8MP sensor featuring 1.12um pixel for the broad smartphone camera markets. This new image sensor supports mainstream selfie imaging, as well as multicamera configurations. The new sensor fits in 5.1 x 6.5mm fixed-focus modules for front-facing cameras. Placing pads on the top and bottom of the sensor also reduced its X dimension, enabling narrow-bezel designs and 4:3 aspect ratios. The OV08B offers Bayer imaging and a 4-cell binning capability for better low-light video performance.
"The 1/4 inch 8 MP sensor category continues to see tremendous volume opportunities in the mainstream mobile phone camera market. In addition to selfie cameras, we are also expecting to see these sensors being deployed in multiple-camera configurations, enabling features such as optical telephoto zoom and ultrawide-angle cameras. The multiple-camera configuration is fast becoming a standard requirement in everything from entry-level to high-end smartphones," said James Liu, product marketing manager at OmniVision. "The OV08B provides the best combination of performance, features, cost and power consumption in a 1/4 inch optical format, and is an ideal option for customers upgrading from 5 MP image sensors."
Samples are expected to be available in April 2019.
"The 1/4 inch 8 MP sensor category continues to see tremendous volume opportunities in the mainstream mobile phone camera market. In addition to selfie cameras, we are also expecting to see these sensors being deployed in multiple-camera configurations, enabling features such as optical telephoto zoom and ultrawide-angle cameras. The multiple-camera configuration is fast becoming a standard requirement in everything from entry-level to high-end smartphones," said James Liu, product marketing manager at OmniVision. "The OV08B provides the best combination of performance, features, cost and power consumption in a 1/4 inch optical format, and is an ideal option for customers upgrading from 5 MP image sensors."
Samples are expected to be available in April 2019.
Light Co. Signs Agreement with Sony
Globenewswire: Light Co. announces the agreement with Sony Semiconductor to jointly work on development and marketing of multi-image sensor solutions. The agreement allows Light to use and recommend to its customers and partners, Sony’s image sensors built in Light’s computational imaging solutions and reference designs. These new reference designs combine Light’s multi-camera technology together with Sony’s image sensors to create new multi-camera applications and solutions beginning with the introduction of smartphones containing four or more cameras.
“Sony is the recognized quality and market share leader in image sensors and we are thrilled to partner with them,” said Dave Grannan, CEO and co-founder, Light. “We are entering an entirely new era of intelligent imaging applications that will transform smartphones, autonomous vehicles, and security systems. With Sony’s world-class image sensors, we can introduce new innovations in the multi-camera imaging space.”
“We are excited to be working with Light and driving multi-sensor-based products and solutions into the market,” said Hank Ochi, president of Component Solutions Business Division, Sony Electronics Inc. “Light and its technology are transforming how devices see the world. This new partnership will allow us to work together to evolve and speed up the design of today’s multi-image sensor enabled connected devices. Starting today, our jointly developed reference designs will help our smartphone OEMs to quickly and easily enhance the imaging capability of multi-camera enabled smartphones.”
“Sony is the recognized quality and market share leader in image sensors and we are thrilled to partner with them,” said Dave Grannan, CEO and co-founder, Light. “We are entering an entirely new era of intelligent imaging applications that will transform smartphones, autonomous vehicles, and security systems. With Sony’s world-class image sensors, we can introduce new innovations in the multi-camera imaging space.”
“We are excited to be working with Light and driving multi-sensor-based products and solutions into the market,” said Hank Ochi, president of Component Solutions Business Division, Sony Electronics Inc. “Light and its technology are transforming how devices see the world. This new partnership will allow us to work together to evolve and speed up the design of today’s multi-image sensor enabled connected devices. Starting today, our jointly developed reference designs will help our smartphone OEMs to quickly and easily enhance the imaging capability of multi-camera enabled smartphones.”
Wednesday, February 20, 2019
Samsung Galaxy S10 5G Features 6 Cameras
Samsung announces S10 generation of its flagship Galaxy phones, including the top of the range 5G model with ToF rear camera. CNET put together a nice table summarizing the camera differences in the S10 family:
"The Galaxy S10 5G truly packs the power of a professional-grade camera into your phone by offering a total of six lenses – two on the front and four on the back. In addition to featuring all of the lenses included in the Galaxy S10+, the 5G model introduces Samsung’s next-generation 3D Depth Camera.
This innovative camera allows the device to accurately capture depth by measuring the length of time it takes for an infrared light signal to bounce off the photograph’s subject. The camera uses the resulting depth information to improve the quality of portrait-style images, and to power exciting new features like Video Live focus and Quick Measure. The former allows you to apply cinema-quality bokeh effects to recorded videos, while the latter enables you to use your phone to instantly measure distance, area or volume."
"The Galaxy S10 5G truly packs the power of a professional-grade camera into your phone by offering a total of six lenses – two on the front and four on the back. In addition to featuring all of the lenses included in the Galaxy S10+, the 5G model introduces Samsung’s next-generation 3D Depth Camera.
This innovative camera allows the device to accurately capture depth by measuring the length of time it takes for an infrared light signal to bounce off the photograph’s subject. The camera uses the resulting depth information to improve the quality of portrait-style images, and to power exciting new features like Video Live focus and Quick Measure. The former allows you to apply cinema-quality bokeh effects to recorded videos, while the latter enables you to use your phone to instantly measure distance, area or volume."
Albert Theuwissen Reviews ISSCC 2019 - Part 2
The second part of Albert Theuwissen's review of image sensor session at ISSCC 2019 talks about “A Data Compressive 1.5b/2.75b Log-Gradient QVGA Image Sensor with Multi-Scale Readout for Always-On Object Detection” by Christopher Young, Alex Omid-Zohoor, Pedram Lajevardi, and Boris Murmann from Stanford University and Robert Bosch:
“A 76mW 500fps VGA CMOS Image Sensor with Time-Stretched Single-Slope ADCs Achieving 1.95 e– Random Noise” by Injun Park, Chanmin Park, Jimin Cheon, and Youngcheol Chae form Yonsei University and Kumoh National Institute of Technology, Korea:
“A 76mW 500fps VGA CMOS Image Sensor with Time-Stretched Single-Slope ADCs Achieving 1.95 e– Random Noise” by Injun Park, Chanmin Park, Jimin Cheon, and Youngcheol Chae form Yonsei University and Kumoh National Institute of Technology, Korea:
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)