- New theory of RTS noise based on multi-atom metastable defects in Si crystal structure
- If correct, it might cause a paradigm shift in the ways to reduce RTS noise
- Opens a way to simulate and analyze various ways of RTN suppression on computer models
- This is my personal favorite of 2021 that hopefully would turn into commercial product achievements in 2022-25
- Gives a hope that RTN would be eradicated in future devices
- Samsung 17nm FinFET process for stacked CIS logic die
- Samsung 2.2V supply pixel is in mass produced 108MP smartphone sensor
- Samsung Advanced Institute of Technology presented its version of 0.8um color-routing pixel
- Sony splits 4T pixel transistors between two layers in a stacked sensor
- SPAD progress:
- Sony created 6um-pitch SPAD with 20.2% QE at 940nm
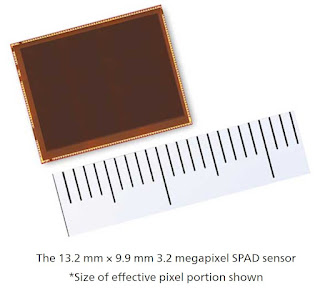
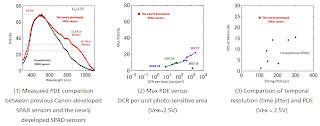
- Canon presented 3.2MP SPAD sensor
- LiDAR SPAC parade continues:
- LiDAR consolidation: Sense Photonics has been acquired by Ouster for $68M in stock with 5-year reverse vesting for key employees
- China News:
- Galaxycore IPO makes CEO Stanly Zhao a multi-billionaire
- High productivity: Smartsens completed more than 30 tapeouts in 2020, 31 tapeouts in 2021, released 36 new products in 2021
- Smartsens IPO at $4.4B valuation
- Tyrafos raised "hundred of millions of yuan" investment
Friday, December 31, 2021
2021 in Review
In 2021, Smartsens Released 36 New Sensors to Mass Production, Completed 31 Tapeouts
Tencent, Sohu: Smartsens reports that in 2021 it has released 36 new products to mass production, and completed 31 tapeouts of future products including 4K and 8K image sensors for security and surveillance applications.
In a separate announcement, Smartsens presents its new automotive sensors: VGA SC031AP and 1MP SC101AP, both integrated with ISP and Tx output port:
Thursday, December 30, 2021
Panasonic Analyses SPAD Quenching
Stratio Combines its SWIR Sensor with AI Algorithms to Detect Fakes
Wednesday, December 29, 2021
CIS Companies Among Largest R&D Spenders in China
JW Insights publishes a list of top R&D spenders among semiconductor companies in China. Image sensor companies Will Semi (Omnivision) and Goodix take 3rd and 5th places respectively:
More About Canon 3.2MP SPAD Sensor
Tuesday, December 28, 2021
Huawei Unveils ISP with AI-based Low-Light Imaging Enhancement
Omnivision Milestones
Monday, December 27, 2021
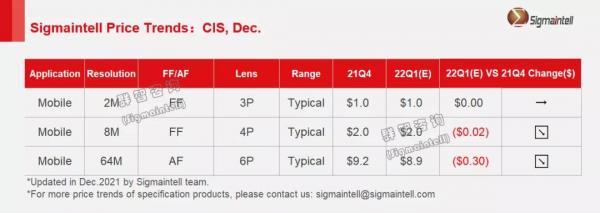
Mobile Camera Module Prices in China in December 2021
Howard Rhodes Lifetime Achievement Memorial
Sunday, December 26, 2021
A3 on Recent Image Sensor Innovations
Association for Advancing Automation (A3) publishes its list of "Image Sensor Innovations that Push Machine Vision Forward."
- ToF sensors:
- Sony DepthSense BSI family
- Teledyne e2v Hydra3D ToF CMOS
- Teledyne e2v Flash series of image sensors for 3D laser triangulation
- Prophesee event-based sensors
- Sony IMX487 UV CMOS sensor
- Sony SenSWIR sensors
- SWIR Vision Systems CQD sensors
- Emberion graphene SWIR sensor
- Gpixel GMAX32103 CMOS sensor achieving 103.7MP resolution at 24fps frame rate
ST Promises SWIR Quantum Dot Pixel Future
Saturday, December 25, 2021
Metasurface Photodetectors Review
MDPI publishes a review paper "Metasurface Photodetectors" by Jinzhao Li, Junyu Li, Shudao Zhou, and Fei Yi from Huazhong University of Science and Technology, National University of Defense Technology, and Raytron (China).
"Typical photodetectors only convert the intensity of light electrical output signals, leaving other electromagnetic parameters, such as the frequencies, phases, and polarization states unresolved. Metasurfaces are arrays of subwavelength structures that can manipulate the amplitude, phase, frequency, and polarization state of light. When combined with photodetectors, metasurfaces can enhance the light-matter interaction at the pixel level and also enable the detector pixels to resolve more electromagnetic parameters. In this paper, we review recent research efforts in merging metasurfaces with photodetectors towards improved detection performances and advanced detection schemes. The impacts of merging metasurfaces with photodetectors, on the architecture of optical systems, and potential applications are also discussed."
Friday, December 24, 2021
Gpixel Announces 9MP 1.1” NIR-enhanced Sensor for Intelligent Traffic Systems
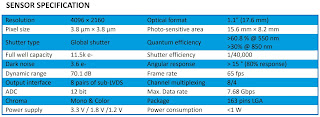
Gpixel announces GMAX3809 extending the GMAX family into ITS applications next to its traditional industrial inspection segment. Gpixel optimized the GMAX product architecture with dedicated ITS features such as enhanced NIR response, pixel size of 3.8 μm, LED flicker mitigation and multiple region HDR modes. GMAX3809 is first in a series of GMAX products with optimized product features for ITS applications.
GMAX3809 fits 4096(H) x 2160(V) (9 MP) resolution into a 1.1” format with low noise, charge domain Global Shutter pixels running at 65 fps at 12-bit ADC resolution. GMAX3809’s 3.8 μm pixel achieves a FWC of 11.5 Ke- and noise of 3.6 e- which delivers more than 70 dB linear DR. The peak QE is 60%, a Parasitic Light Sensitivity is -92 dB, and angular response at > 15° is 80%.
GMAX3809 comes standard in a NIR-enhanced version using Gpixel’s Red Fox technology, offering the ultimate balance between NIR sensitivity and MTF. GMAX3809 achieves a QE of more than 30% at 850 nm and 14% at 940 nm.
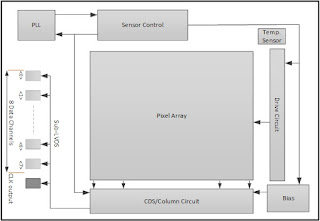
GMAX3809 delivers 65 fps with 8 pairs of sub-LVDS channels each running at 960 Mbps resulting in a maximum data rate of 7.68 Gbps. On-chip functions, such as on-chip color offset calibration, channel multiplexing, multiple region HDR and LED flicker are available and programmable through SPI or I2C interface.
GMAX3809 is housed in a 163-pin ceramic LGA package with outer dimensions of 27.1 mm x 17.9 mm. The sensor assembly includes a double side AR coated cover glass lid.
GMAX3809 engineering samples can be ordered today for delivery in January, 2022.
Thursday, December 23, 2021
BYD QVGA Sensor Won "China Chip" Excellent Market Performance Award
Image Sensors at 2022 Photonics Spectra Conference
- KEYNOTE: Quanta Image Sensors: Every Photon Counts, Even in a Smartphone
Eric Fossum from Dartmouth College talks about the quantum image sensor concept and how it has been implemented in CMOS image sensors and SPADs and what the major differences are between culminating results. - Emerging Short-Wavelength Infrared Sensors
Matthew Dyson from IDTechEx Ltd. examines the motivation and applications for SWIR image sensing, and assesses the opportunities, challenges, and adoption roadmap for emerging technical approaches. - LEDs: Expanding Capabilities for Live Cell Imaging
Isabel Goodhand from CoolLED explains how innovations such as multi-wavelength switching and TTL triggering enable faster imaging, and how multi-band filters can balance speed and contrast requirements. - Advanced Detector Solutions Enabling Quantum Optics Research
Colin Coates from Andor Technology presents high-performance detector solutions that are central to fundamental research on entangled photon systems and ultracold quantum gases. - How Pixel Size and MTF Affect Modern Microscopy and See the Invisible with Microscopes
Gerhard Holst from Excelitas PCO GmbH discusses the role of camera pixel size and MTF in the design and application of modern microscopes. - Enabling Rapid Application Development and Deployment of Hyperspectral Imaging in a Production Environment
William Rock from Headwall Photonics Inc. presents on the utility of hyperspectral imaging in a production environment using examples in food processing and demonstrates the expedited development cycle using novel hardware and software. - High-Throughput Hyperspectral Imaging without Image Degradation
Rand Swanson from Resonon Inc. examines the problem of image degradation with hyperspectral imagers and explores approaches to enhance the signal. - New Photon-Counting Detectors Expand Frontiers in Scientific Imaging
Jiaju Ma from Gigajot Technology Inc. explains the fundamentals of photon-counting image sensors, or quanta image sensors, beginning with the background knowledge necessary to effectively apply these devices. - Dynamic Photodiodes: Unique Light-Sensing Technology with Tunable Sensitivity
Serguei Okhonin, ActLight SA. Tunable sensitivity sets dynamic photodiode apart from all existing photodiodes, including SPADs. The AI in dynamic photodiode technology is able to dynamically adjust sensitivity at the pixel level to adapt to changing light conditions and keep the high precision of depth measurements. This presentation elaborates on the concept and design of these emerging photodiodes and how they are set to impact today’s sensing applications. - Current and Future Detector Designs for Flash Lidar
Jennifer Ruskowski, Fraunhofer IMS. The roadmap for creating lidar sensors for autonomous cars and robots is moving into a new era. Becoming ever more important are technologies such as sensor fusion and embedded AI, which are poised to enhance the performance, efficiency, and acceptance of lidar sensors. Additionally, on a hardware level, lidar components such as laser sources and detectors are becoming increasingly powerful. Jennifer Ruskowski gives a brief overview of the Fraunhofer IMS’s lidar development activities, from light detector to system design to sensor fusion and embedded AI solutions. - FMCW and TOF Flash Automotive Lidar: Challenges and Prospects
Slawomir Piatek, New Jersey Institute of Technology & Hamamatsu Corp. A vision of self-driving cars propels research and development for automotive lidar, vital hardware providing distance and velocity information about car surroundings. Among several lidar concepts—with some already adopted and heading toward production for automotive advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and industrial markets—two newer designs have emerged with the highest potential in the future: frequency-modulated continuous wave (FMCW) lidar and time-of-flight (ToF) flash lidar. Both concepts, however, face engineering challenges impeding full adaptation. This presentation reviews operation principles of each technique and then discusses in greater detail the unique challenges each one faces. In particular, a light source with a long and stable coherence length is the primary challenge of FMCW lidar, whereas a photodetector with high photosensitivity and low noise is the challenge for ToF-flash lidar. The presentation concludes with a review of possible solutions to the aforementioned obstacles.
Recent Videos: Light Co., Harvard University, Sony
Light Co. publishes a video presenting its automotive stereo camera advantages over LiDAR featuring Guidehouse Principal Analyst Sam Abuelsamid, VP at Co-pace Continental AG Anil Rachakonda, Light CEO Dave Grannan, and Light's Chief Product Officer Prashant Velagaleti:
Politecnico di Milano publishes Harvard University's Federico Capasso lecture "Meta Optics: From Flat Lenses to Structured Light and Dark:"
Sony publishes 3 videos on its Pregius S stacked global shutter sensors (1, 2, 3):
Tuesday, December 21, 2021
Trieye Unveils VCSEL Powered SWIR Camera
PRNewswire: TriEye announces "the first of its kind VCSEL powered Electro-Optic (EO) SWIR system", integrating TriEye CMOS-based sensor with VCSEL as an illumination source.
TriEye demonstrates an EO system by integrating the TriEye Raven with 1350nm SWIR VCSEL-based illumination, provided by their VCSEL partner, as such they enable the highest power density - which today is over 5 watts per mm2 . This new EO system will provide significant value for short-range applications such as mobile, biometrics, industrial automation, medical and more.
TriEye's solution is said to be the first to provide SWIR based sensing using VCSEL technology. TriEye's SWIR system opens doors to next generation perception capabilities by providing a significant value proposition compared to the NIR spectrum. This includes resilience to sunlight and other sources of ambient noises while providing an eye-safe illumination source. With this combination, the perception system will have longer range and better accuracy than previously achievable with NIR based systems.
Monday, December 20, 2021
NTT Demos 0.84um Color-Routing Pixel
NTT Device Technology Lab publishes an OSA Optica paper "Full-color-sorting metalenses for high-sensitivity image sensors" by Masashi Miyata, Naru Nemoto, Kota Shikama, Fumihide Kobayashi, and Toshikazu Hashimoto.
"Image sensors play a critical role in current technologies ranging from smartphones to autonomous vehicles. In these technologies, high-sensitivity image sensors are highly desired because they enable dark-scene/ultra-fast imaging. Unfortunately, a conventional sensor architecture that employs color filters on every pixel fundamentally limits the detected light power per pixel because of the filtering, which has been a long-standing barrier to sensitivity improvement. Here, we demonstrate polarization-insensitive metasurface lenses (metalenses) that sort primary colors on high-density pixels without the use of color filters. The metalenses simultaneously act as pixel-scale color splitters and lenses and are compatible with complementary metal–oxide-semiconductor sensor technology. An image sensor with such metalenses significantly enhances the detected light power, while affording high image quality, incident angle tolerance, and sub-micrometer spatial resolution. The demonstrated architecture opens the way to the development of high-sensitivity color image sensors that exceed current limits while maintaining consistency with state-of-the-art sensor technology."